Research projects

A digital inquiry platform for wicked problems (2025-2029)
Development of a digital platform dedicated to the multi-disciplinary resolution of complex problems. In collaboration with the University of Lausanne.
Partner : The project is carried out in collaboration with the Visual Collaboration Lab at the University of Lausanne, headed by Professor Stéphanie Missonier.
This 4 years research project is funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF).
Lire la suite ▼
Problem
Wicked problems are characterised by their challenging formulation and resolution, the lack of single or definitive solution, a contrasting view from their stakeholders, and the likelihood that any given solution will lead to other problems.
Solution
Our project aims at exploring the potential of combining physical (paper-based) and digital (digital inquiry platform) artefacts to integrate Visual Inquiry Tools and systems thinking approaches.
Our focus will initially be directed on a specific wicked problem of major importance: pivoting existing businesses towards greater social and environmental sustainability, which involves the sustainability assessment of business models.
A multidisciplinary approach will be used, with the integration of elements from management sciences and computer sciences, including knowledge domains such as design sciences research, sustainable business model, system thinking, visual inquiry tools, web technologies, usability and user experience.
Benefits
By combining paper-based and digital tools, our project will develop pragmatic solutions for addressing wicked problems of our contemporary world, and training the next generation to address them.
Lire moins ▲

Major Incidents Medical Management Simulation (2021-2025)
This 4 years research and development project aims at developing a global software simulation for training in emergency medicine. The realization of the project will lead to advances in simulation training and digitization of education. The solution will allow the preparation of health professionals for the management of exceptional events.
Partner: Geneva University Hospital (HUG)
The project is co-funded by the Geneva University Hospital and InnoSuisse.
Lire la suite ▼
Problem
In the field of emergency medicine, the concept of Major Incident Medical Management and Support (MIMMS) is applied when rescuers are faced with a number and type of injuries requiring the use of unusual means. The way rescue teams operate changes radically from the daily routine and some actors have to take on coordination roles that are non-existent in their traditional activity. There is a need to train responders in these different professions.
Solution
The proposed solution is a digitalization of training, with a new type of software simulation, offering flexibility in training management and the creation of simulation scenarios, as well as support for debriefing and analysis of participant behavior.
The development of the solution involves advances in several areas. The simulation environment must be adaptive to allow flexibility in training modes. An authoring system must allow non-computer specialists to create complex scenarios. A learning analytics system must allow the analysis of individual and collective performance. A dashboard must allow the trainer to follow and adapt in real time the progress of the simulation.
Benefits
The implementation of this solution improves the preparation of professionals for the management of major events while helping to reduce training costs. This better preparation increases the victims’ chances of survival and reduces costs and trauma due to poor management of the event.
Lire moins ▲

Patient’s Rights & Innovative Teaching Strategy (2020-2022)
The Patient’s Rights & Innovative Teaching Strategy project aims at developing a Serious Game whose purpose is as much to support students in learning the legal rules applicable in the field of heath, as to broaden the pedagogical options of teaching and learning.
Partner: Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud (HESAV).
This project is financed by the HES-SO digital skills centre.
Lire la suite ▼
Problem
For health professional, implementing patient rights in practice is not easy. Many situations combine legal, ethical and health problems. Studies show that awareness of patients’ rights is not sufficient to guarantee their application in health care practice.
Solution
A multi-disciplinary collaboration between health, law, pedagogy and engineering will enable the development of a software simulation game for practical training to patients rights.
Benefits
The software simulation will allow both training of students and post-training of healthcare professionals. A constructivist pedagogical approach will allow skills development based on the lived experiences in simulation and debriefing sessions.
Lire moins ▲
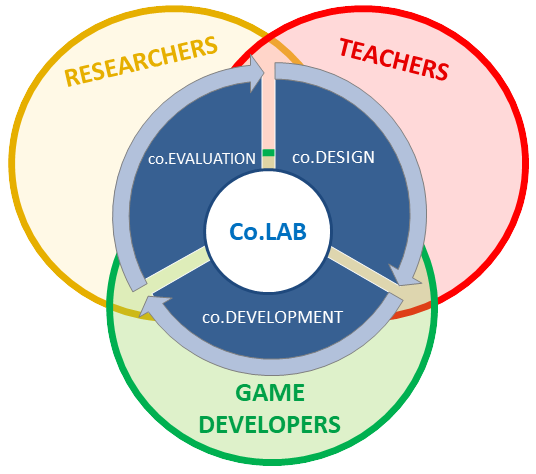
co.LAB – A digital platform for the collaborative development of learning games (2020-2024)
The co.LAB project (A Digital Lab for the co-Design, co-Development and co-Evaluation of Digital Learning Games) has been elected for a four-year grant by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF) in the frame of the NRP 77 programme “Digital Transformation”.
The co.LAB project aims to set up a methodological framework for collaboration between teachers, game developers and researchers in educational sciences, supported by a collaborative digital platform dedicated to the co-design, co-development and co-evaluation of digital learning games.
Responsible applicant: Prof. Dominique Jaccard, Albasim, MEI, HES-SO
Main project partner: LIP (Laboratoire d’Innovation Pédagogique, UniFR, Prof. Eric Sanchez)
Lire la suite ▼
Problem
Interest in Digital Learning Games (DLGs) has increased at all levels of education. DLGs have positive impacts such as increased students’ motivation and engagement and are effective tools to support learner centered teaching practices.
However, the use of DLGs remains a problem due to the gap between teachers, software developers and researchers. Co.LAB is an interdisciplinary development research project (computer sciences & educational sciences) aiming at enabling a relevant and ethical implementation of DLGs at all educational levels in Switzerland.
Solution
The objective of the project is to develop a methodological framework and a digital platform for the co-design, co-development and co-evaluation of DLGs. The methodology and the digital infrastructure will be implemented in a laboratory dedicated to design-based research grounded on the collaboration between teachers, game designers, computer scientists and researchers in educational sciences. The development and evaluation in real school contexts of a showcase game dedicated to computational thinking will serve as a proof of concept. Co.LAB elaborates on a mixed methodology based on learning analytics and focus groups with participants.
Benefits
The Co.LAB digital platform and methodology should help to increase relevance and efficiency in Digital Learning Game design and development.
Co.LAB may serve both as an example of the introduction of digital in education and as a basis for future co-development of digital learning resources in general.
Lire moins ▲

«Serious games» in higher education (2019-2020)
The objective of this project is to explore, test and disseminate the potential for educational innovation brought by serious games in university education.
This project is funded by the DIKU (Norwegian Agency for International Cooperation and Quality Improvement in Higher Education), who promotes development and innovation in education, encourage international cooperation and digital learning methods.
Partners: University in Agder, Norway

« Emergency Triage » – A serious game to evaluate the impact of environmental distractors on the performance of emergency triage (2018-2019)
In the emergency department, triage decisions have a direct impact on patients’ survival rates. However, studies have found significant differences in nurses’ attribution of emergency degrees, with major consequences on patient management.
Partners: Institut et Haute Ecole de santé La Source, Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève (HUG)
Funding : HES-SO
Lire la suite ▼ Problem Among the factors that could explain the cause of discrepancies in triage decisions, distractors in the work environment such as noise or task interruptions were highlighted but did not benefit from specific investigations, particularly due to the difficulty of evaluating them in real healthcare environments. But the actual effect of these distractors is still poorly understood. Solution Develop and use a serious game in order to reproduces a work environment with distractors and provide a unique opportunity to explore their impacts on the quality of triage in emergency departments. Benefits This study will provide a better understanding of the contribution of the work environment to safe care. Lire moins ▲

H2020 : M-Benefits (2018-2021)
Industrial and service sectors offer potential for cost-effective energy-savings. But under-investment in energy-efficiency is observed in all EU countries. This is called the «energy-efficiency gap».
In this project, AlbaSim is the task leader for the development of the serious games that will be used for training of energy-efficiency experts and for results dissemination.
Funding: European Commission – Horizon 2020
Lire la suite ▼
Problem
Why don’t companies increase investment in energy efficiency? One answer is that project proposals usually focus only on energy savings, which is not the core business of most firms.
However, by quantifying and communicating all benefits – improved product quality, enhanced productivity, better indoor environment – proposals become competitive.
Solution
Establish a database of case studies and develop a methodology that helps assess multiple benefits of energy efficiency.
Develop a serious games to train energy experts to evaluate all effects of energy efficiency measures.
Benefits
This work will contribute to increase attractiveness of energy projects and to reduce the energy-efficiency gap.
Lire moins ▲

Peroll’Ard – a game for animating an open doors day (2018)
Peroll’Ard is a game created together with the Laboratoire d’Innovation Pédagogique (LIP) for the 2018 open doors day of University of Fribourg (Switzerland). The game is designed for smartphones and seeks to encourage visitors to discover the animations organized by the different departments on that day.
Lire la suite ▼
Inspired by the world of witchcraft, the game consists of collecting points and clues by visiting the booths to solve a puzzle. This online application allows players to discover the University’s missions in a fun way. Play is indeed a metaphor for academic work: it is the development and transmission of knowledge that makes it possible to respond to the great challenges facing humanity.
QR-code scanning inside the game allows the player to participate to geolocalized quizzes. The data collected during this full-scale experiment (traces of interactions at the booths and answers to quizzes) are currently being processed. The aim is to assess the usability of the current version of the game and understand how the visit was perceived by visitors of the open doors day. It is also about understanding how the game can contribute to a better promotion of the University’s missions.
The game was primarily created by Simon Morard using the Wegas authoring platform during his Master’s thesis.
Lire moins ▲

PACT – Playing & Computational thinking (2018)
PACT is a joint project with University of Fribourg (Switzerland) and gymnasium teachers, which is funded by the Hasler Foundation. PACT aims at offering innovative game-based learning resources to secondary school teachers in computer programming.
The LIP group of University of Fribourg and the Albasim group are collaborating on the design, development, implementation, analysis and dissemination of game-based programming education.
Lire la suite ▼
Three categories of research questions are addressed:
- Acceptability of the resources produced by the project: Do the students develop strategies demonstrating that they are engaged in addressing the computational challenge offered by the game?
- Usability: Do they face difficulties? Which difficulties?
- Usefulness: Do the strategies implemented demonstrate that the student/player has developed knowledge related to computational thinking?
Expected outcomes:
- Innovative teaching resources for computational education,
- Frameworks for innovative teaching scenarios supported by research results,
- Experienced teachers ready for acting as computing ambassadors and trainers of other teachers,
- Empirical evidences on the relevance of a game-based learning approach to the development of computational thinking.
Members of the PACT project: Eric Sanchez (UNIFR-LIP), Dominique Jaccard (HEIG-VD), Jarle Hulaas (HEIG-VD), Maud Plumettaz-Sieber (UNIFR-LIP), Christian Brodard (Collège de Gambach), Laurent Bardy (Collège St Michel), Laurence Fidanza (Collège du Sud), Cédric Donner (Collège du Sud), Andre Maurer (GYB), Samuel Vannay (LCC).
Lire moins ▲

GesTerre (2017)
Development of a serious game in the field of governance and territorial development. This simulation is used in graduate programmes and continuing education.
Partners: Environmental Governance and Territorial Development, University of Geneva

TraumaSim – acute care (2016)
Development of a simulation for health care training. The simulation can be used both in presential and distant learning.
Innovation: coupling distant simulation software activities with presential virtual patient interactions.
Partners: Department of Nursing Sciences of Fribourg (HEdS-FR), Switzerland.

Corporate law (2015)
Objectives: Development of a serious game in the field of corporate law
Innovation: Develop active pedagogy with large audience. Use of a peer review processes inside the serious game.
Partners: Faculty of Law, University of Geneva

Clinical Cardiac Assessment (2014)
Objectives: Development of a serious game in the field of clinical cardiac evaluation
Innovation: Use of a serious game as both a practical exercise and a trigger for individual learning.
Partners: La Source, Institut et Haute Ecole de la Santé

Sustainable urbanism (2013)
Development of a serious game for sustainable urbanism education.
Partners: Faculty of Geosciences of the University of Lausanne, TRIBU architects

Project Management Game (2012)
Development of a serious game in the field of project management education.
Results: Thousands of students and project managers have been trained with the PM-Game in bachelor, master and postgraduate studies, in many universities and companies like HES-SO, X Polytechnique Paris, University of Lausanne, University of Geneva, Cnam, University of Marseille, Centre d’Education Permanente du Canton de Vaud, or Ecole Hotelière de Lausanne.
Innovation: This simulation was the first project management simulation including all phases of a project (initiation, planning, execution, closure), with a authoring content editor enabling trainers to create customized scenarios.

Web Game Authoring System (Wegas) (2012)
Objectives: Development of an authoring system for creation, edition and diffusion of serious games.
Results: Wegas is an open source web-based game authoring and execution platform. This authoring system is both an applied research project in itself and a research infrastructure for co-development and distribution of serious games. Wegas serves as the basis for a broad range of serious games developed in collaboration with universities in Switzerland and abroad, and is currently annually used by thousands of students.
Wegas includes many innovations. It was probably the first web authoring system enabling the creation, content edition and distribution of serious games.
Partners: HES-SO











